Different Types of Hipped Roof Designs
On This Page
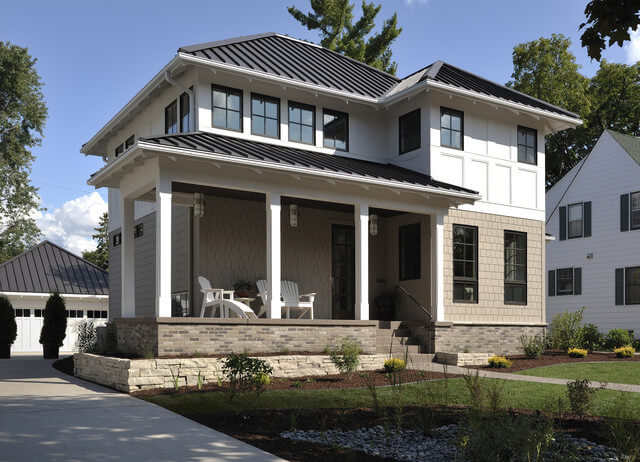


7 Different Types of Hipped Roof Designs
A hipped roof, also known as a hip roof, is a roof design type where all sides slope down to the walls, forming a continuous and even plane around the building. In other words, a hipped roof has no vertical ends or gables. Instead, the roof ends are angled inward towards the ridge of the roof, creating a pyramid-like shape.
Hipped roofs are commonly used in residential and commercial construction because they offer several advantages, such as better stability, durability, and resistance to wind and weather. They also provide more attic space and a more uniform appearance than other types of roof designs. However, hipped roofs can be more complex and expensive to construct than simpler roof designs, such as flat or gabled roofs.
Most Common Hip Roof Types
Simple Hip Roof
This is the most common type of hipped roof. It has four sloping sides meeting at the ridge, forming a pyramid-like shape. The roof has a uniform slope, and no gable ends or vertical walls. It is a versatile design and is used for a wide range of building styles, from traditional to modern.
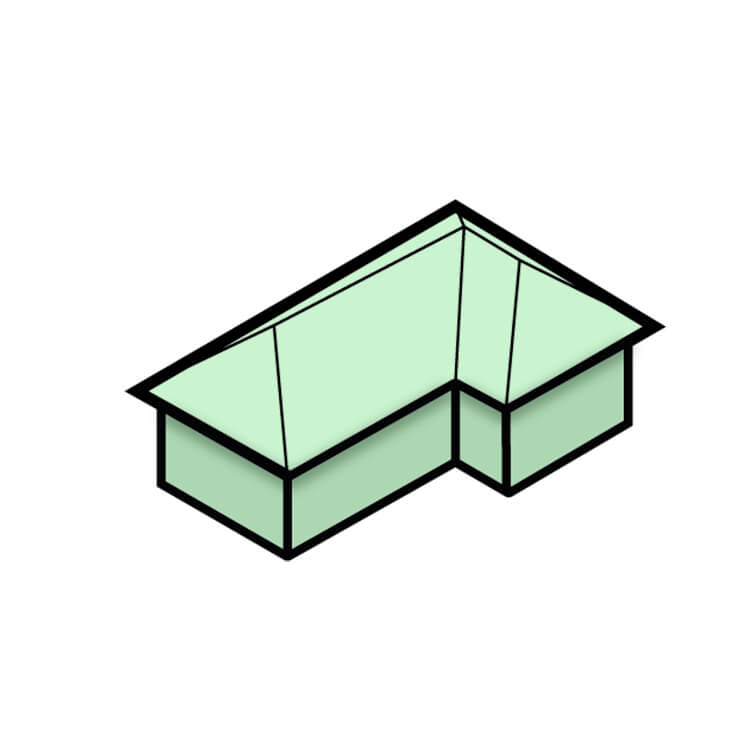
Cross-Hipped Roof
This type of hipped roof has two or more hip ridges that intersect at different angles, creating multiple roof sections. The design is often used for buildings with L-shaped or T-shaped footprints, allowing each roof section to have a uniform slope. This design can be more complex than a simple hip roof, but it adds visual interest and can help break up the mass of a larger building.
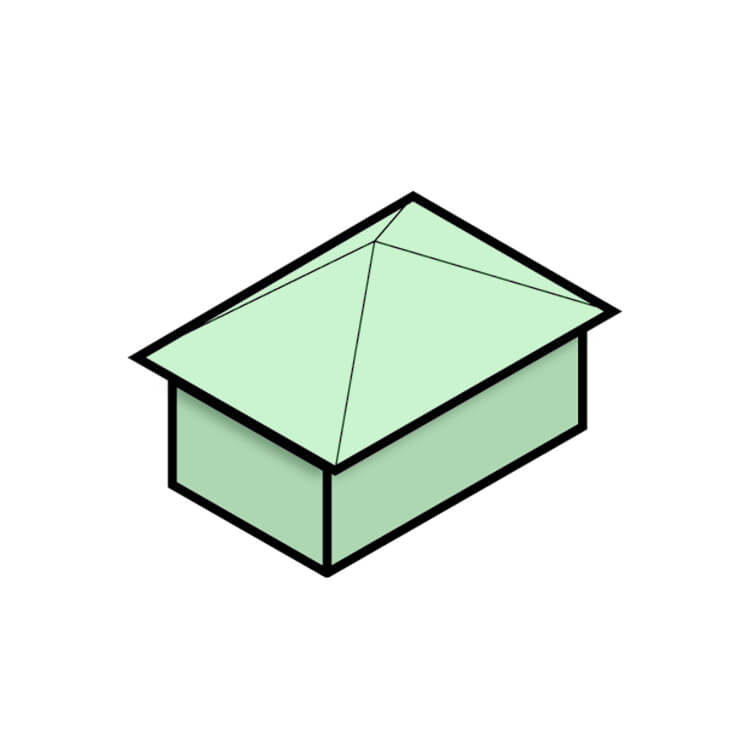
Pyramid Hip Roof
A pyramid hip roof is a hipped roof with a square footprint, where all sides slope downward to the centre point, creating a pyramid-like shape. This simple and elegant design is often used for smaller buildings such as cottages or bungalows but can also be used for larger structures such as churches or public buildings. Its uniform slope provides excellent stability in high winds and efficient water drainage through a central gutter or downspout.
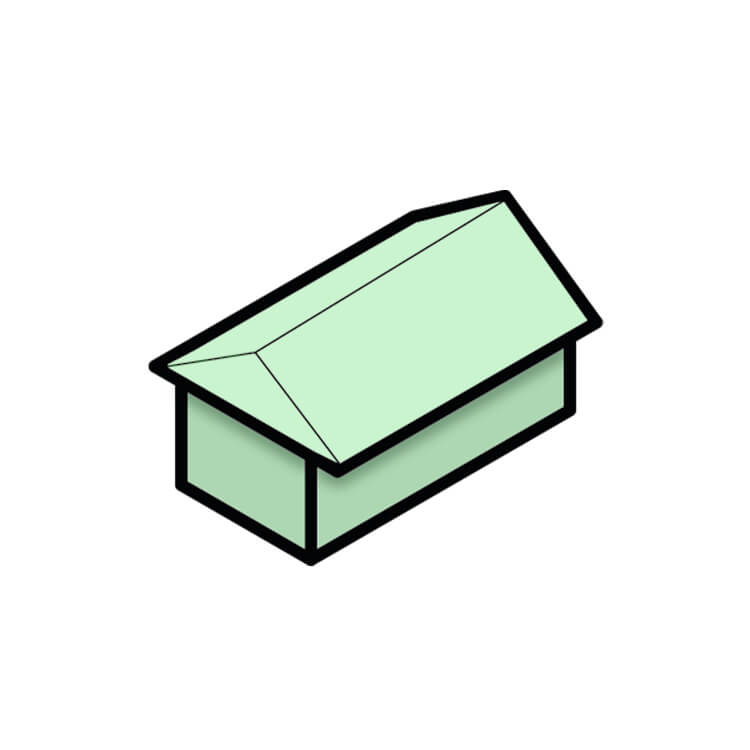
Half-Hipped Roof
This variation of the simple hip roof has gable ends that are partially truncated, creating a small vertical wall at the end of each roof slope. This design is often used for buildings with a more traditional or cottage-style appearance, adding charm and character to the roofline. The half-hipped roof is also more stable in high winds than a standard gable roof.
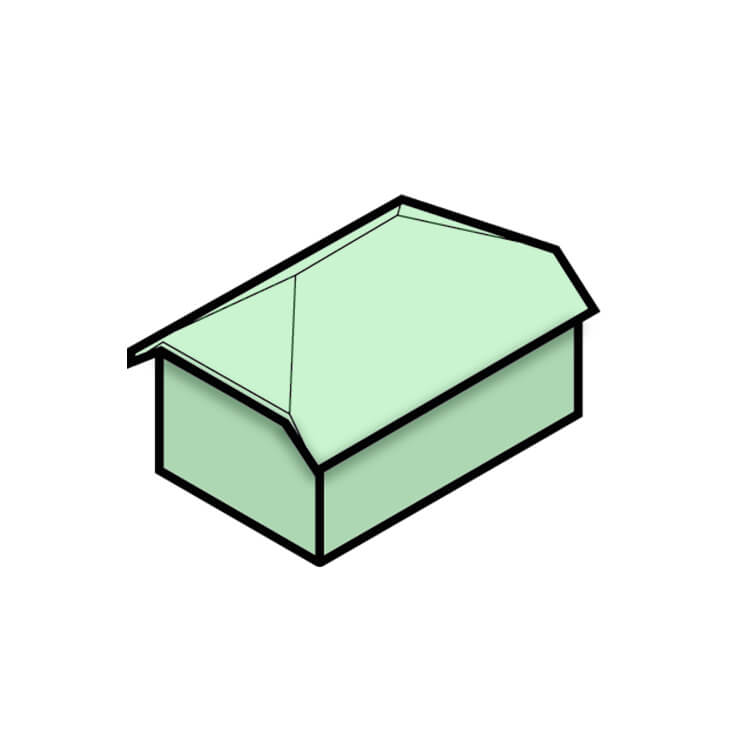
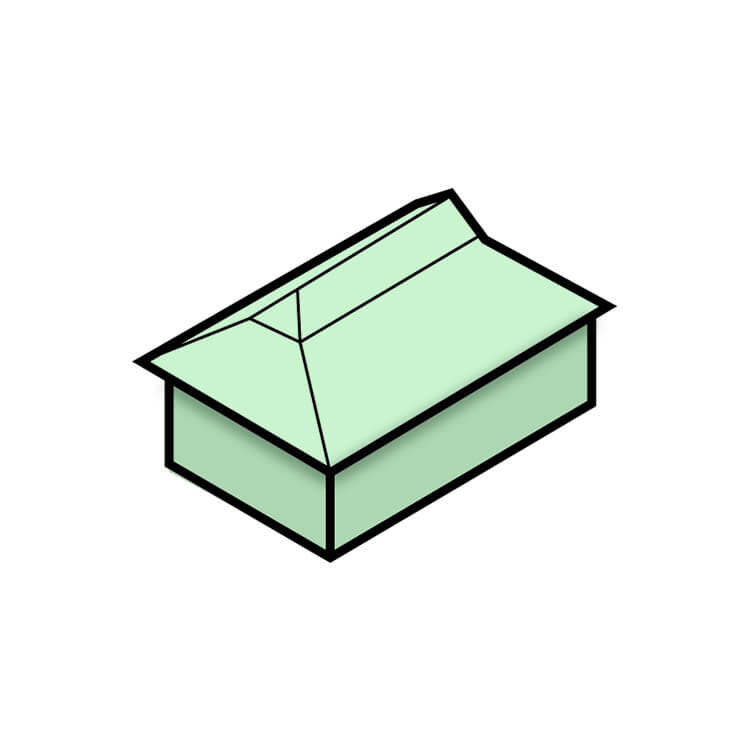
Mansard Roof
This type of hipped roof has two slopes on each side. Its lower slope is steeper than the upper slope. This design allows for more living space in the attic, making it a popular choice for French architecture. Mansard roofs are also common in urban areas, as they can provide additional living space in buildings with height restrictions.
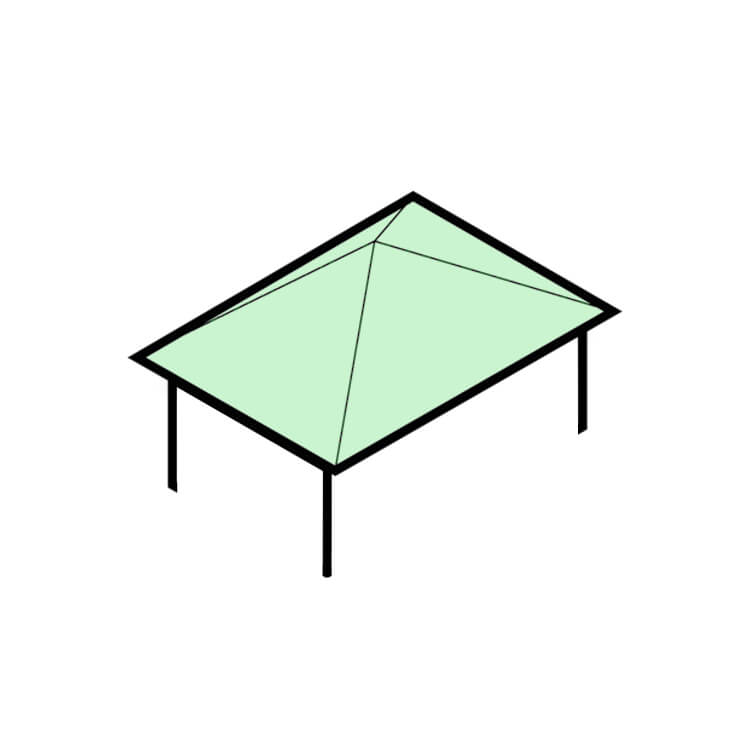
Pavilion Roof
This is a simple hipped roof with a square or rectangular footprint, often used for small structures such as gazebos or pavilions. The roof has a low pitch and is supported by a central post or column. This design provides shade and shelter while maintaining an open and airy feel.
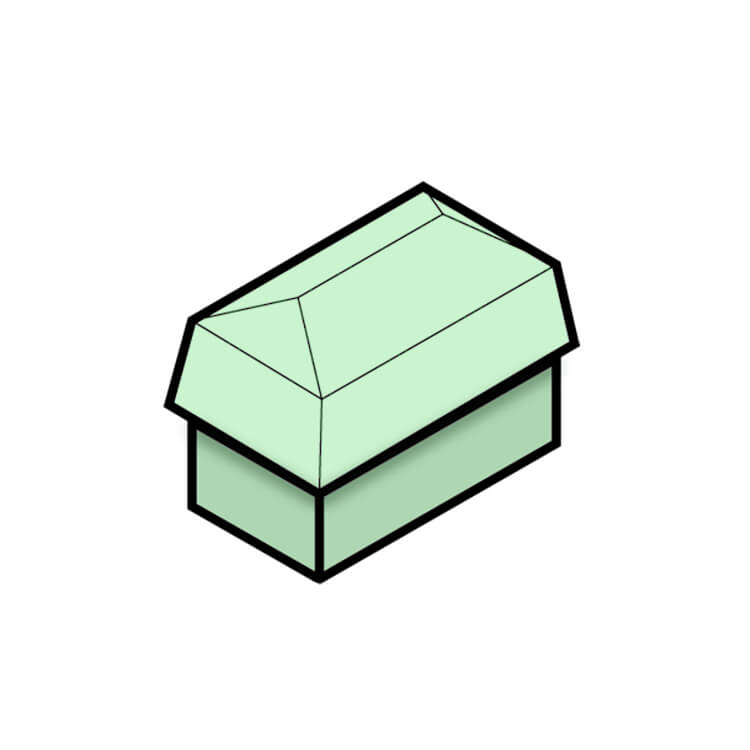
Dutch Gable Roof
This hybrid design combines elements of a gable roof and a hipped roof. The gable end of the roof is extended with a hipped roof section, creating a unique and attractive look. This design is often used for residential buildings, particularly in Dutch Colonial architecture. The Dutch gable roof provides additional attic space and can be more stable in high winds than a standard gable roof.


Advantages of the Hip Roofs
Hip roofs offer several benefits over other types of roof designs, including:
Stability: Hip roofs are more stable than gable roofs because all sides slope downward, which provides better support against strong winds and severe weather conditions.
Good Drainage: The slopes on all sides of a hip roof allow rainwater to drain off easily, reducing the risk of leaks or water damage.
Energy Efficiency: Hip roofs provide more insulation and ventilation than other roof types, which can help reduce heating and cooling costs.
Additional Living Space: Hip roofs can be designed with dormers or other structures that allow for additional living space in the attic, which can increase the house’s functionality.
Aesthetically Pleasing: Hip roofs have a classic, timeless look that can add curb appeal to a home and complement a variety of architectural styles.
Suitability of Hip Roofs with Different Factors
Hipped roofs are suitable for various building types and styles, including residential, commercial, and industrial structures. Some of the factors that make hipped roofs a good choice for certain properties include:
- Climate: Hipped roofs are particularly suitable for areas that experience high winds, heavy rain, and snow loads. The sloping sides of the roof provide better resistance to wind uplift and water penetration, and the weight distribution is more evenly spread, making them more resilient to heavy snow loads.
- Architectural Style: Hipped roofs are commonly used in traditional and classic architectural styles, such as Georgian, Colonial, and Victorian, where they provide a timeless and elegant look. However, they can also be used in modern and contemporary designs, where they create a sleek and minimalist appearance.
- Building Size and Shape: Hipped roofs work well on buildings with rectangular or square footprints, where they provide a balanced and symmetrical appearance. They are also suitable for buildings with multiple wings or extensions, where they can be used to tie together different rooflines.
- Structural Support: Hipped roofs require more structural support than simpler roof designs, such as flat or gabled roofs. Therefore, they are best suited to buildings with strong load-bearing walls and foundations.
